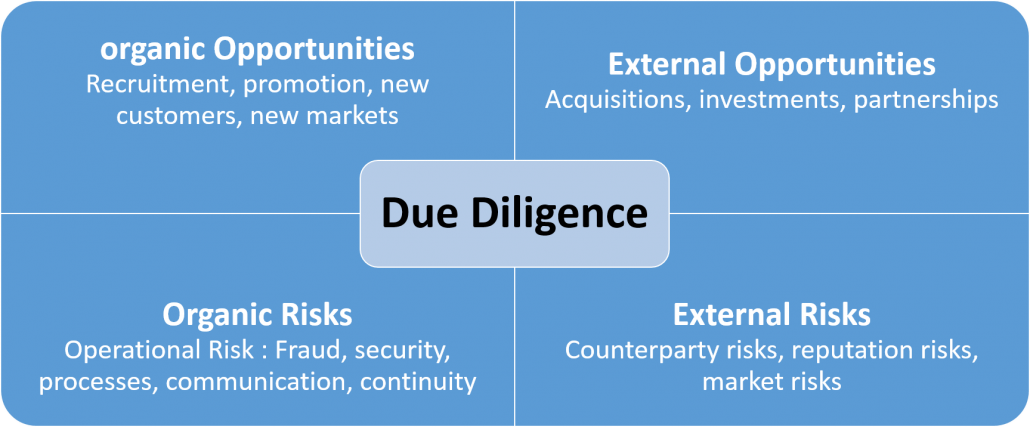
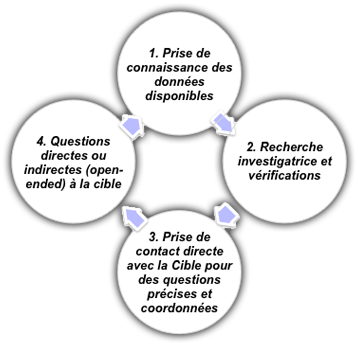
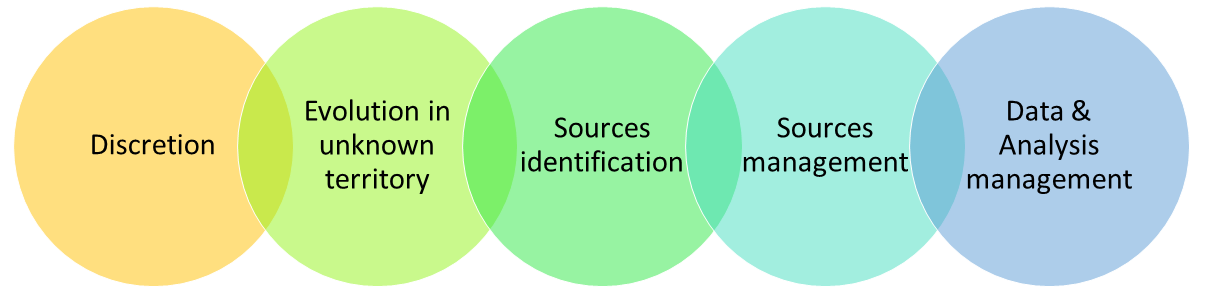
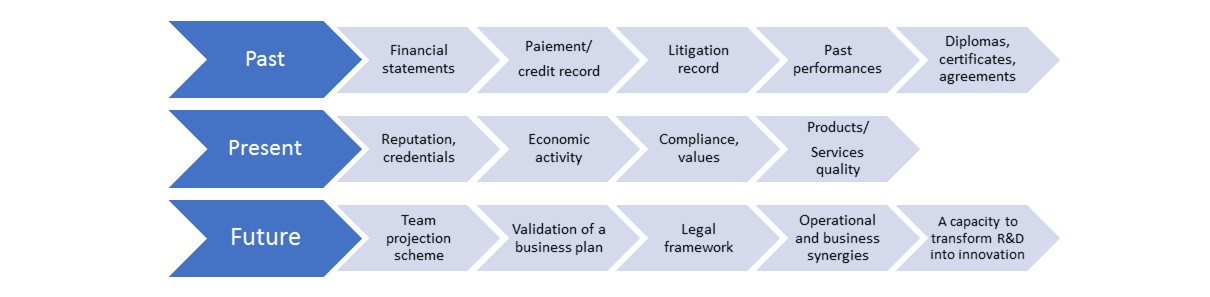
Areas of major risks in partnerships or joint ventures are especially those involving foreign partners, hidden defects, misunderstandings, differences and ulterior motives, or failure to comply with applicable laws.
Any of these elements can lead to a difficult and costly conflict, which may result in termination of the agreement, partnership or merger, and the potential liability of the company is engaged.
National laws sometimes require a principal “sponsor” local partnership operates and holds a majority stake.
Partnerships and joint ventures with offshore companies also require special precautions.
Risks can occur for various reasons. In some business circles corruption is endemic.
An activity deemed inappropriate by the exporting firm from a partner may, in certain circumstances, exposing others to risk.
The mutual ignorance of company policies often are the source of counterparty risk.
Risks can occur for various reasons. In some business circles corruption is endemic.
An activity deemed inappropriate by the exporting firm from a partner may, in certain circumstances, exposing others to risk.
The mutual ignorance of company policies often are the source of counterparty risk.